“The First World War”
The MAIN cause that led to World War I
Militarism (a race to build bigger and better armies and fleets than other countries)
Submarines, tanks, gas, machine guns, and aeroplanes were some of the weapons that European countries had that made war deadlier.
Alliances are deals between groups of people to help each other out in times of war.
Alliances were made between groups of countries to balance out the power of others.
Imperialism means getting involved in other countries’ politics and economies in order to get rich and powerful.
They fought for territory in Asia and Africa because they needed raw materials.
Nationalism is the belief that one group of people, a language, or a society is better than all others.
Groups that are controlled by other countries fight to be free.
Allies Before the War
Triple Alliance: Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy
Triple Entente: Russia, Britain, and France
The spark that began the war
The assassination:
Archduke Franz Ferdinand, who was heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary, was killed by a Serbian patriot.
What made this lead to war? Austria-Hungary went to war with Serbia. Russia decided to protect Serbia because they had a deal together before. They got the military ready for war by mobilising it. So…
Germany went to war with France and Russia, which made Britain go to war with Germany. This made Austria-Hungary go to war with Russia.
Who’s is on which side now?
Austria-Hungary and Germany were the two main powers.
Britain, France, Russia, and Italy were all Allied Powers.
**Note: Italy fought on both sides in 1915!
The War in Europe
Unlike other wars, European militarism brought new technologies to both sides that helped them, especially:
Machine Guns

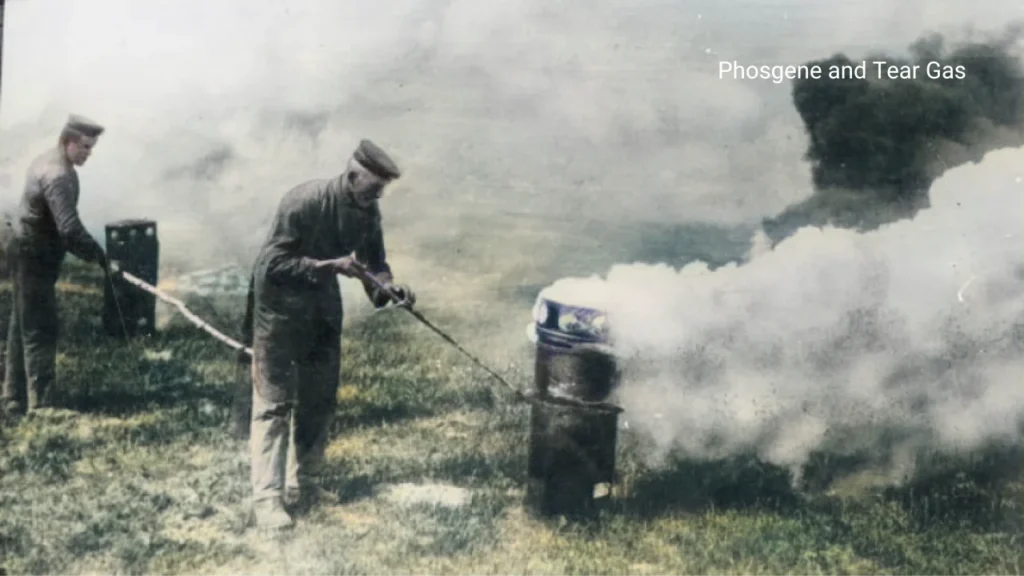
Poisonous Gases

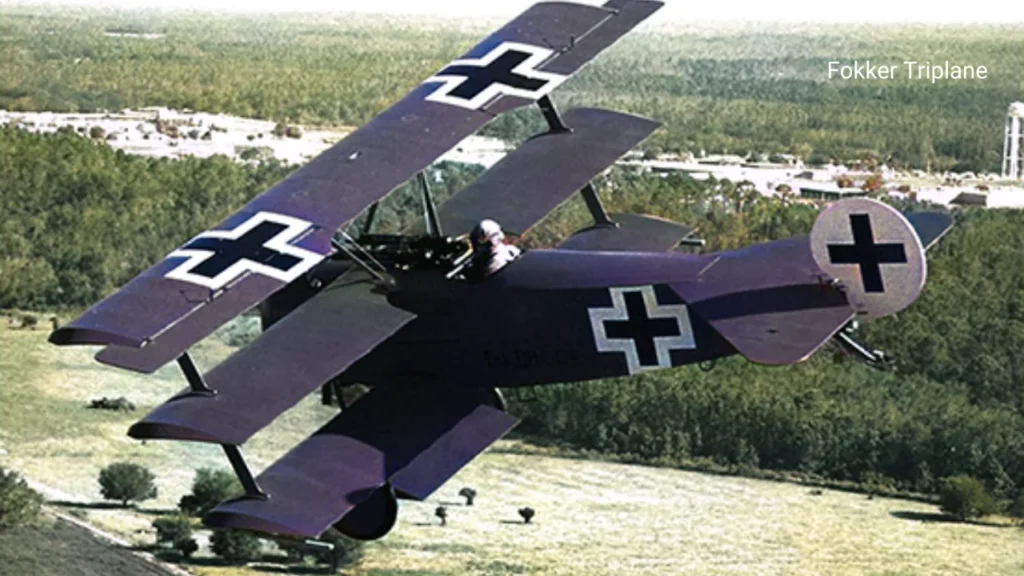
Airplanes

U-Boats (submarines)
They also came up with new strategies, like trench warfare: where they defended a position by fighting from deep trenches.
No-man’s-land was the area between the two lines. This is where a lot of the fights happened.
What must the US do? Stay out of the war or start one?
Why neutrality is good
- Who wants to war?!
- A lot of people thought the war was about things in Europe, not the United States.
- Many Americans came from countries in the Central Powers, even though most of them supported the Allies.
- A lot of money was made by American companies during the war, especially when they sold goods to the Allies.
That’s right, the war was already over by the end of 1914—neither side could win a clear victory.
So how do we get involved?
- The Sinking of the Lusitania: The Lusitania was a British ship with 128 Americans on board. It was sunk by German U-boats during the First World War. Americans are getting more and more angry that German subs are sinking civilian ships.
- The Zimmerman Case Note: The German minister to Mexico suggested that Germany and Mexico work together to fight the US. Mexico would get the land that is now New Mexico, Arizona, and Texas in exchange for their work. People in the US learned about this and are very angry about it.
We start a war with Germany on April 6, 1917!
The United States at Home During the First World War
- The War Industries Board was made to keep an eye on how the things made by the country’s war industries (steel, copper, rubber, etc.) were made and sent to customers.
- It was the job of the Committee of Public Information to get more people to back the war effort. They tried to make the case for why the US should be in the war.
- ll men between the ages of 21 and 30 had to sign up for the draft when Congress passed the Selective Service Act. Each draft number was picked at chance.
- People bought Liberty Bonds to get money to buy goods for the allies.
- The Food Administration made the US make more food to feed its friends, and the Fuel Administration made more coal, gas, and oil.
- Workers knew that the lack of workers gave them the chance to go on strike and demand higher pay and better working conditions. To keep workers from going on strikes, the National War Labour Board settled disagreements between workers and managers.
Role of Women:
Women played an important role. They did housework and offered to be nurses and ambulance drivers in the army.
Bringing about peace
Russia left the war in 1917, and the US joined it. The war ended when a ceasefire (truce) was signed in November 1918.
The European After the Battle
- There were more than 20 million hurt/killed and more than 8 million dead troops.
- The countries involved lost all of their money.
- Damage was done to land and houses all over Europe. The damage to property was more than $30 billion.
France, Great Britain, and Germany were all owed money.
Wilson’s Fourteen Points
- President Wilson came up with a plan for peace terms that would not be too hard on the Central Powers and would not cause another war. This plan was called Wilson’s Fourteen Points. The Fourteen Points was the name for these.
- Most of the Points were about specific countries or areas. Some called for ships to be free on the seas, troops and navies to be smaller, and secret deals between countries to end.
- Stressed Self-Determination, which is the right of each person to choose their own political situation. This means that the people could handle their own politics instead of letting an outside power decide what to do.
- It was suggested in the last point that an international gathering called the League of Nations be set up to settle disagreements and protect democracy.
Wilson’s Fourteen Points were not liked by many people in the US and Europe. They wanted to get back at the Germans.
Paris Peace Conference
- Wilson, Lloyd George, Clemenceau, Orlando, and other leaders like them get together at the Paris Peace Conference to work out the terms of peace.
- Each of them has different ideas about what to do, so they fight. Wilson isn’t able to get them to agree with all fourteen points.
- Other leaders all say that Germany needs to pay for the costs and damage caused by the war. This is called “reparations.” Cost all together: $33 billion. Some of the land that Germany had won in the war was also split up.
The Treaty of Versailles was finally put forward. Some of the Fourteen Points were in it, especially the right to self-determination. A lot of new countries were made, and the Allies took over the Central Powers’ old colonies.
There are issues with the League of Nations
Setting up the League of Nations was the most important part of the Treaty to President Wilson. It would have people from democratic countries on it, and they would work together to settle disagreements to support peace.
Even so, the Senate did not agree with the Treaty of Versailles and did not approve it. They were afraid that the US would become too close to Europe if it joined the League of Nations. America didn’t get much out of the war, but it did lose tens of thousands of young people. The US signed a separate peace deal with the Central Powers in the end.
Effects of WWI
- The US joined the war in 1917.
- Millions of lives and a lot of damage in Europe
- The Treaty of Versailles
- The German and Austro-Hungarian Empires fell apart.
- Making a number of new states
- The League of Nations


